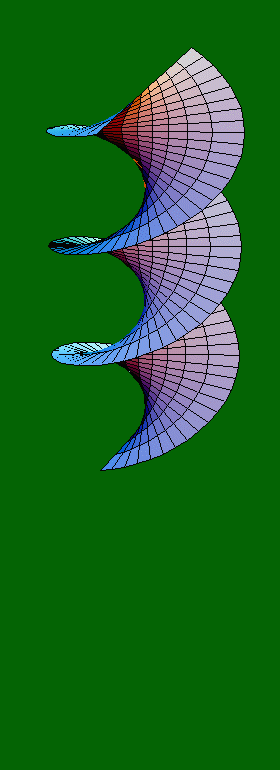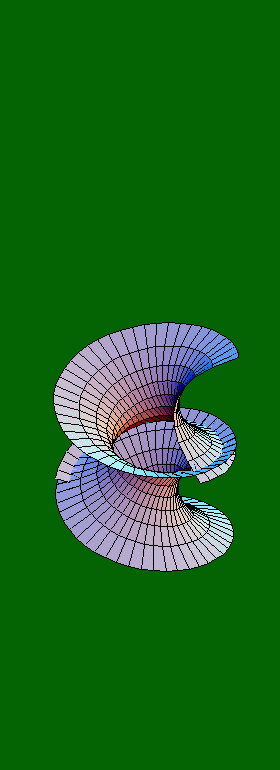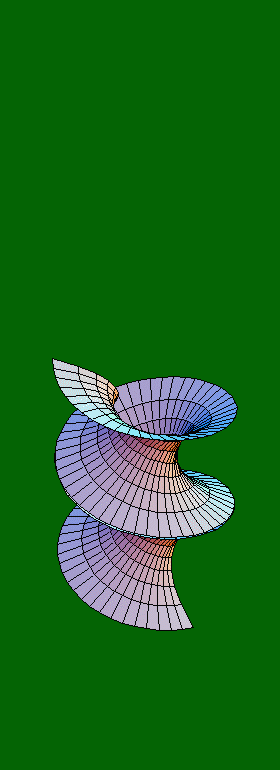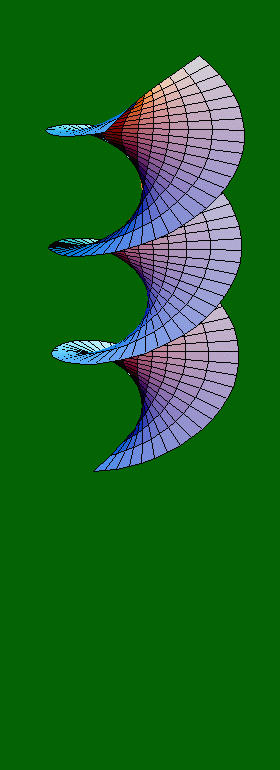
x(u,v) = cos(á) sinh(v) sin(u) + sin(á)
cosh(v) cos(u)
y(u,v) = -cos(á) sinh(v) cos(u) + sin(á) cosh(v) sin(u)
z(u,v) = u cos(á) + v sin(á)
where:
- á is a parameter ranging from 0 to 2ð, giving the 80 frames shown here with a step of ð/40
- u ranges from 0 to 3ð, resulting in the three folds of the surface
- v ranges from -ð/2 to ð/2, defining the diameter of the "cylinder" within which the surface lies.
Note: The values ð/2 and 3ð/2 for á result in a catenoid (a 2-D rendering of which is produced when we hold a flexible string, or chain, from its two ends, and keep it loose). All other values for á result in a helicoid.
References:
Weisstein, Eric W. CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics, pp. 205-206